Wind speed distribution and flow characteristics
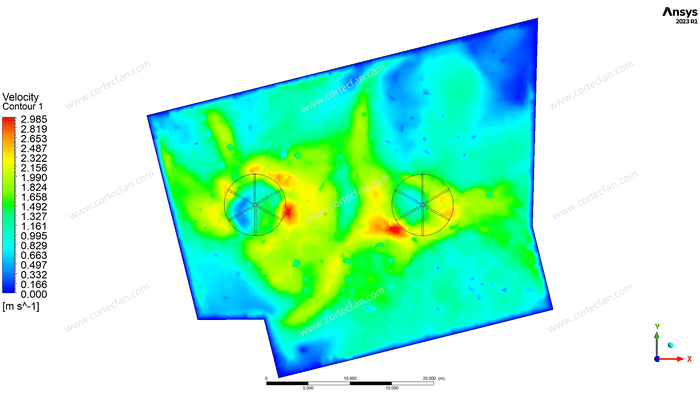
From the first CFD simulation diagram, we can see that the wind speed distribution shows a clear gradient change. The red area in the figure represents the area with higher wind speed, while the blue area is the area with lower wind speed. Since the HVLS Fan generates a large airflow when running, the wind speed is higher in the area close to the fan and gradually decreases toward the periphery. This design allows the fan to cover a larger area and avoids the problem of local air flow being too strong or too weak.
The fan rotation area in the wind speed profile creates a vortex-like airflow pattern. This vortex effect helps to evenly distribute the air. The fan not only acts on the area around it, but also affects the farther parts of the space, helping the uniformity and expansion of the air flow. This makes HVLS Fans very suitable for use in large space ventilation solutions.
3D airflow pattern and volume rendering analysis
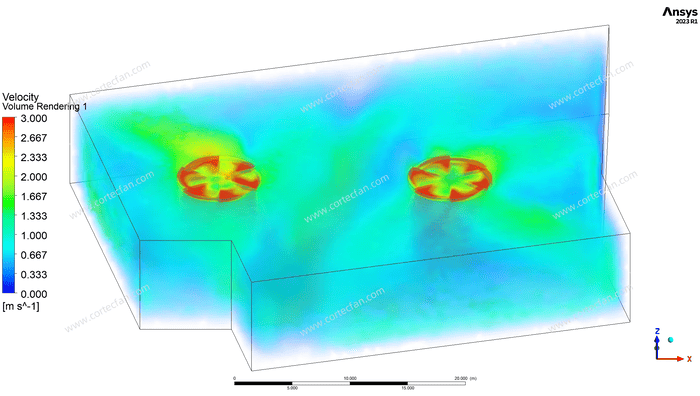
The second picture shows a more detailed wind speed distribution map through volume rendering. It can be seen that in the rotating area of the fan, the airflow is obviously affected by the fan blades, forming a strong vortex structure. These vortices can effectively diffuse the air and prevent air from being trapped in a certain local area. In addition, the volume rendering also shows the flow characteristics within the fan's range of action. The wind speed gradually expands from the core area of the fan to the entire space, showing the advantages of the HVLS Fan's fluid mechanics performance in a large space. This airflow scalability makes the HVLS Fan more efficient than traditional high-speed, low-volume fans in large-area environments.
Wind speed variation and energy efficiency optimization
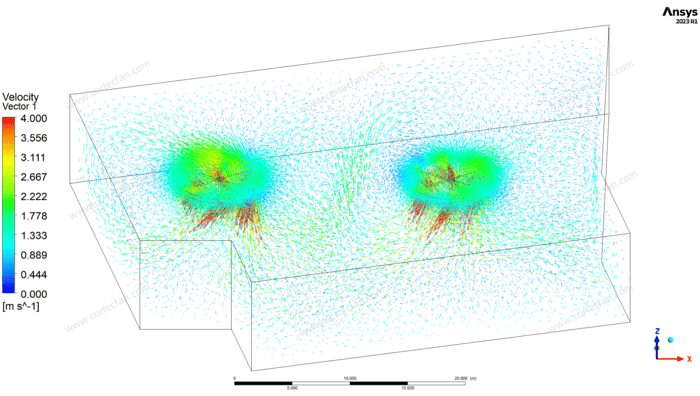
The third wind speed profile shows how the wind speed changes in different areas. As can be seen from the figure, the wind speed increases rapidly in the center of the fan and reaches the maximum value, while the wind speed gradually decreases in the area away from the fan. This change in wind speed gradient shows that the air flow generated by the fan is uniform.
Through further analysis of the wind speed distribution, designers can adjust the fan speed and angle according to the actual needs of the space to further optimize air flow and energy efficiency.
Summarize
As a low-speed and high-efficiency ventilation device, HVLS Fans can provide uniform air flow in large spaces, improve air quality, and reduce energy consumption of air conditioning systems through their unique design principles. Combined with CFD simulation results, we can see the excellent performance of HVLS Fans in fluid mechanics. And by specially designing the blades and adjusting the shape and angle, HVLS Fans can provide the best ventilation effect in different application environments.


